Dirt Work Knowledge
Understanding Dirt Work: The Essential Guide
Dirt work, also known as earthmoving or excavation, is a fundamental aspect of various construction, landscaping, and development projects. It involves the manipulation, excavation, and shaping of soil, rock, and other materials to create desired topographies, foundations, and landscapes. Whether you're preparing a site for construction, grading a road, or landscaping a property, having a solid understanding of dirt work is essential for successful project execution.
Key Concepts in Dirt Work:
- Site Preparation: Before any construction or landscaping project can begin, proper site preparation is crucial. This involves clearing vegetation, debris, and other obstructions, as well as grading the land to ensure proper drainage and stability.
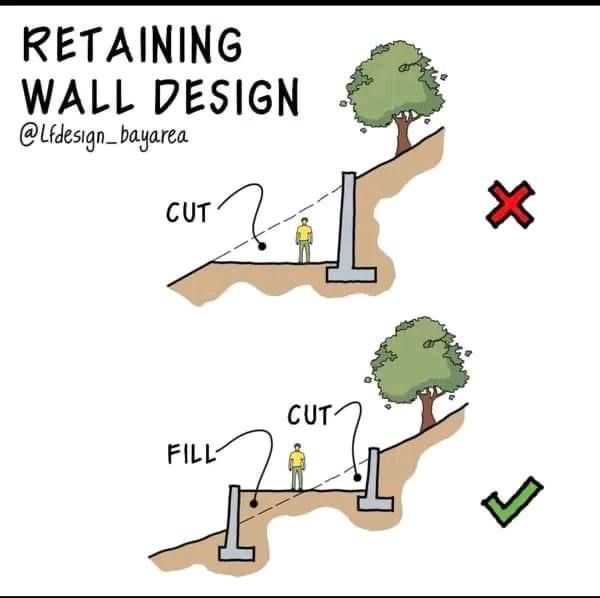
- Grading: Grading is the process of shaping the land to achieve a desired slope, elevation, or contour. It involves cutting into high areas and filling in low areas to create a level surface or achieve a specific grade. Proper grading is essential for drainage, erosion control, and the overall aesthetics of the landscape.
- Excavation: Excavation involves the removal of soil, rock, or other materials from the ground to create trenches, foundations, or underground utilities. Excavation work must be done carefully to avoid damage to existing structures, utilities, and the surrounding environment.
- Compaction: Compaction is the process of compressing soil to increase its density and stability. Proper compaction is essential for ensuring the structural integrity of roads, foundations, and other structures built on the soil.
- Erosion Control: Managing erosion is critical in dirt work projects to prevent soil loss, sedimentation, and environmental damage. Techniques such as installing erosion control measures, using erosion-resistant materials, and establishing vegetation can help mitigate erosion and preserve soil health.
- Equipment and Machinery: Dirt work requires specialized equipment and machinery to efficiently move, excavate, and shape soil and other materials. Common equipment includes bulldozers, excavators, loaders, graders, and compactors, each with its own capabilities and applications.
Skills and Expertise in Dirt Work:
- Knowledge of Soil Types: Understanding the properties of different soil types, such as clay, sand, and gravel, is essential for effective dirt work. Factors such as soil composition, moisture content, and compaction characteristics influence excavation, grading, and compaction techniques.
- Safety Awareness: Dirt work involves working with heavy equipment and machinery in potentially hazardous environments. Proper safety training, adherence to safety protocols, and awareness of potential hazards are essential for preventing accidents and injuries on the job site.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Dirt work projects often present unforeseen challenges and obstacles that require quick thinking and problem-solving skills. The ability to adapt to changing conditions, troubleshoot issues, and find innovative solutions is invaluable in the field of dirt work.
- Attention to Detail: Precision and accuracy are crucial in dirt work to achieve the desired grades, slopes, and contours. Paying attention to detail and maintaining high-quality workmanship ensure that projects meet specifications and regulatory requirements.
- Environmental Awareness: Environmental considerations play a significant role in dirt work projects, particularly in sensitive ecosystems or areas prone to erosion. Minimizing soil disturbance, implementing erosion control measures, and preserving natural features are essential for environmental stewardship.
Conclusion:
Dirt work is a foundational aspect of many construction, landscaping, and development projects, requiring knowledge, skill, and attention to detail to achieve successful outcomes. By understanding key concepts, mastering essential skills, and prioritizing safety and environmental stewardship, dirt work professionals can contribute to the creation of durable, functional, and sustainable landscapes and infrastructure.
All Rights Reserved | Contract Service Group | Powered by Flypaper | Privacy Policy
